Health Information System Architecture Harmonized And
Health Care Information Systems Architectural Models And

Enterprise architecture (ea) is a management tool that provides means for aligning information systems with organisation's mission, goals and objectives. ea is . This program transforms applicants with it and computer science backgrounds into health information system architects for health information systems design and . Architecture of health it. these hospital health information system architecture information systems are designed to serve narrow functions with great efficiency, but this situation results in multiple silos of information. it is more useful to collect all the information on a patient in a single location. to accomplish this, health care organizations often have clinical data.
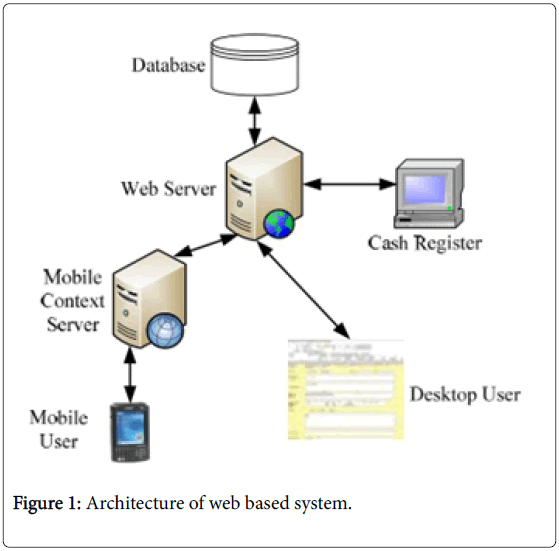
Health information health information system architecture system architecture describes the fundamental organization of the system embodied in its components, standards, and principles governing its design and evaluation. this builds on the underlying logic of all systems. More health information system architecture images. The information system for a single hospital is best built around a multi-tiered client-server local area network (lan) architecture.
A Robust Health Data Infrastructure
Thereby helping to realize the promise of a robust health data infrastructure. any hit system for health care must strive to balance these countervailing demands. 1. 5 a new software architecture the various implementations of data formats, protocols, interfaces, and other elements of a hit system should conform to an agreed-upon specification. To enroll in the health information systems architecture graduate certificate program you’ll need an undergraduate or graduate degree in health information system architecture computer science or in a closely related field, with a strong programming and database skill set. through your classes, you’ll gain both theoretical and hands-on knowledge of health information system design. @inproceedings{stansfield2008thecf, title={the case for a national health information system architecture ; a missing link to guiding national development and implementation}, author={s. stansfield and n. orobaton and d. lubinski and steven uggowitzer and h. mwanyika}, year={2008. Technology that support health information systems advanced in technological complexity, the data that is being received and processed has also become complex. from numeric data through alphanumeric data to imaging and even molecular data (maojo & martin-sanchez, 2004). health information systems infrastructure and information flows.
At the center of this landscape is the person seeking health, surrounded by health system building blocks (health worker, information, governance, etc. ). an outer ring contains organizations, such as care providers (hospitals, day care facilities, etc. ), manufacturers of medical devices, or producers of pharmaceutical products. To accomplish this, health care organizations often have clinical data repositories which pull data from all the separate specialized hospital information systems . Oct 1, 1998 through such approach, the hcr can be considered as an aggregation health information system architecture of (parts of) the information available in the information system, being .
Health Information System Architecture Harmonized And
The Standard Healthcare Information Systems Architecture And The
The european committee for standardization (cen) standard architecture for healthcare information systems (env 12967), health informatics service architecture or hisa is a standard that provides guidance on the development of modular open information technology (it) systems in the healthcare sector. 19 relations. Davis (1982). page 3. tan et al. / information architecture: the case of a nhs hospital. thirty fourth international conference on information systems, milan 2013 .
The acrc has the following specialist groups; data and web engineering, e-learning technologies, e-world, enterprise security management, health informatics, information systems, intelligent systems, knowledge and software engineering, systems architecture and security, wearable computers. Osi, hisa and middleware models: the hisa (healthcare information system architecture) is represented in the middle. the model on the left is referred to osi (open systems interconnection) protocol.
term supply strategies, forecasting silvicultural stock, determining harvesting system options, and more for example intelligis has been used as a building block within the south africa’s forestry industry for a complete gis solution health and human services insurance: insurance companies have implemented gis to visualize, analyze, and manage portfolio risk landscape architecture law enforcement and criminal justice: information about the location of a crime, incident, suspect, Health care information systems: architectural models and governance paolo locatelli, nicola restifo, luca gastaldi and mariano corso politecnico di milano, fondazione politecnico di milano and ihco italy 1. introduction health care is an information intensive industry (rodrigues, 2010), in which reliable and. Abstract. although the demand for use of information technology within the healthcare industry is intensifying, relatively little has been written about guidelines to optimize it investments. a technology architecture is a set of guidelines for technology integration within an enterprise. the architecture is a critical tool in the effort to control information technology (it) operating costs by constraining the number of technologies supported.
Architecture design: components. the information system for a single hospital is best built around a multi-tiered client-server local area network (lan ) . A centralized health information architecture offers economies of scale and reduces costs through a central data repository. but it is less responsive to local needs and has a longer implementation timeline. a decentralized architecture is quick to deploy and adaptable to local needs, but it leads to redundancies and higher costs while limiting the ability to create a larger picture of any one health information need. The use of middleware to develop widely distributed healthcare information systems (his) has become inevitable. however, the fact that many different platforms . Strong health information systems support greater transparency and accountability by increasing access to information. unfortunately, many low and middle-income countries have a long way to go to achieve these goals. federated health information architecture: enabling healthcare providers and policymakers to use data for decision-making.
Similar systems have been developed for radiology, billing, pharmacy, and other services. these hospital information systems are designed to serve narrow functions with great efficiency, but this situation results in multiple silos of information. it is more useful to collect all the information on a patient in a single location. An ihia is described over 3 levels comprising of the “social system”, “application” and “data. ” another key building block of the. ihia is the data warehouse, that .
Healthinformationsystem (his) is the basis of the health system and the key to making evidence-based health policy decisions [1]. it is the intersection of healthcare's business processes and. Health information systems: architectures and strategies is a definitive introductory resource that tackles the pivotal role of information systems in health care. illustrating the importance of information systems in delivering high-quality health care at the lowest possible cost, this book provides the essential resources needed by the health. Functional requirements the system architecture is designed to support all his applications discussed earlier and achieve the following objectives: allow data communications between all applications and users of the entire system. ensure quick response to requests and completion of transactions (fast system performance) ensure business continuity (almost 100% up-time through sufficient.